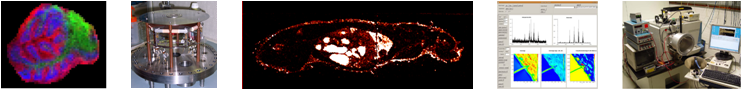
The COMPUTIS project is focused on Molecular imaging in tissues and cells by computer-assisted innovative multimode Mass Spectrometry.
Mass Spectrometry Imaging (MSI)
Mass Spectrometry Imaging (MSI) is a rapidly expanding technology that provides information-rich data on various classes of biomolecules (proteins, peptides, lipids and metabolites), pharmaceutical compounds and toxins directly in tissue at the micrometer scale.

Recent technological advances have enabled sub-cellular spatial resolution and sub-femtomolar sensitivity opening up a whole new level of biological applications.
MSI in 2005
At the advent of the COMPUTIS project, MSI was a rapidly-growing field which was hampered by several key limitations:
- Need for development and optimization of MS technologies such as ion detectors, separation, desorption-ionisation advancements enabling increased sensitivity and spatial image resolution.
- Sample preparation methodology such as tissue hadling and automation methods for matrix application.
- Limited range of biological application - increases in sensitivity and spatial information would open MSI to further applications within the proteomic, metabolomic, genomic, lipidomic fields.
- Bioinformatic and Data processing tools - more detailed data results in larger data files. Advanced data mining tools were required to obtain the required information from both the MS data and image files.
- Standardization of data formats (with HUPO) - due to the different propietary data formats used by the MS instrument vendors, the exchanging of data within collaborations and consortia was often problematic.
These were all concerns which were addressed during the duration of the COMPUTIS project. The results of which have been published in leading scientific journals and presented at international conferences .
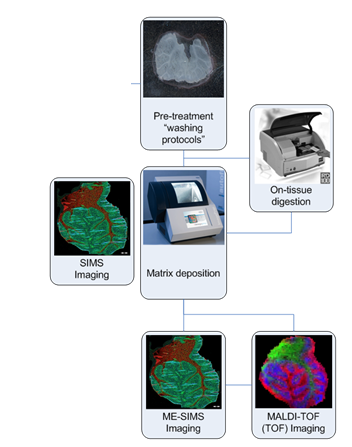
The COMPUTIS Project
COMPUTIS was a 4 year European FP6 project (2006-2009) aimed at developing analytical and software technologies for MSI, combining various methods of SIMS and MALDI.
The three principle objectives of the project were:
- Innovation in MSI instrumentation (desorption, ionization and detection techniques)
- Development of advanced diagnostic methods to identify diseases by study of molecular images
- Monitoring of therapeutic effect on damaged or abnormal cells and tissues
The COMPUTIS project was developed by a consortium of 7 partners consisting of 5 research institutes (1 private) and 2 companies who brought a range of expertise to enable the project aims to be realized :
The project was divided into 8 technical work packages corresponding to the main objectives:
Development of improved instrumentation and experimental protocols
- WP1: Sample selection and preparation
- WP2: Instrumentation development
- WP3: Analytical studies
Development of algorithms and software tools
- WP4: From signal to data
- WP5: From data to knowledge
- WP6: Biological applications
- WP7: Industrial concepts
- WP8: Dissemination and exploitation
Highlighted results
Some of the main results obtained during the duration of the COMPUTIS project are highlighted below:
- imzML data standard for MSI
- High resolution imaging with LTQ-FT and FT-ICR
- Position sensitive delay-line detector for C60 SIMS MSI
- Cluster ion sources to increase sensitivity and resolution of TOF-SIMS
- Matrix spotter for MALDI profiling
- Imaging penetration of drugs into lung granulomas caused by tuberculosis
- Lipid marker of Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Follow-up of gene therapy treatment in MDX mice
- Software for MSI data visualisation & processing
Further details of results obtained during COMPUTIS can be found in the workpackage summaries.