| Workpackage 1: Sample Preparation |

|

|

|
|
Workpackage 1 reviews the choice and the characterization of several chemical compounds which will be utilized along the program as references for (ME-) SIMS and MALDI mass spectrometry and mass spectrometry imaging. The objective is to enhance the performance of MALDI and SIMS mass spectrometry towards their imaging capabilities. Peptides, proteins, lipids, polymers and oligosaccharides are mapped with MALDI with the help of MALDI matrices, while lipids are mapped with SIMS with and without coating. In all the cases these compounds can be used either as calibrants or to adjust the mass spectrometer parameters. The compounds are separated in six classes:
All these compounds, as well as the reference spectra, are available all along the duration of the project to characterize and test the ion desorption methods, instrument performances in terms of sensitivity, mass resolution and/or spatial resolution. The second deliverable reviews the choice and the characterization of reference biological samples which will be utilized along the program as references for SIMS and/or MALDI mass spectrometry and mass spectrometry imaging, as well as their most utilized samples supports, sample preparation methods, sample storage, etc…One important accomplishment is that silicon wafers have been agreed by all the involved partners to become the reference sample support for the future of the project. This material brings together several important and necessary features, flatness, conductivity, purity, adhesion of samples, as well as a moderate price and an excellent reproducibility.  Samples (12 µm thick sections) deposited onto a Silicon wafer (2 inches diameter) Nevertheless, some of the other sample supports, which were previously utilized by the different partners, will still continued to be utilized for particular cases (e.g. optiTOF plates for the fixation of whole-body tissue sections). Concerning the standard samples, a general agreement has been found during the meeting held in Gif-sur-Yvette in December 2006 for rat brain tissue sections and several well known and well characterized cell lines.  A rat brain section (thickness 12 µm) deposited on a silicon wafer Characteristic spectra and images of the reference biological samples are provided In a report. Some examples are given below: 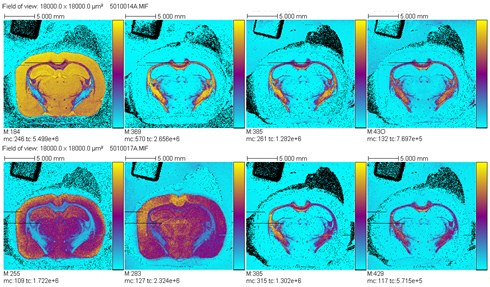 Image recorded over an area of 18x18 mm² at the surface of a rat brain tissue section, 256x256 pixels, pixel size 70x70 µm². Primary ion Bi3+, Primary ion dose density 1E9 ions.cm-². The name of the compounds or the m/z value of the peak centroid, the maximal number of counts in a pixel (mc) and the total number of counts (tc) are written below each image. The color scales correspond to the interval [0, mc] 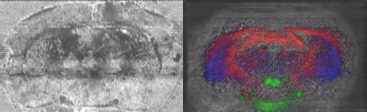 High resolution MALDI stigmatic ion optical images of a tissue section of a male Wistar rat. Pixel size = 600 nm and spatial resolution = 4 mm. (Red: m/z 1857; Blue: m/z 1755, Green: vasopressin 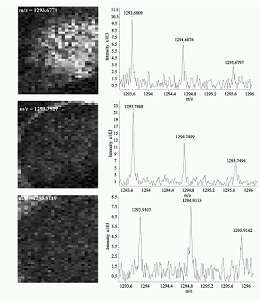 High mass resolution FT-ICR imaging on rat brain sections 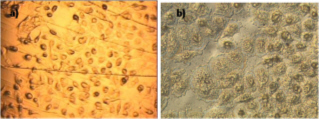 A: Light microscopic images of human renal cancer cells on gold-plated target. Before (a, 650 x 500 µm) and after (b, 320 x 250 µm) addition of matrix (DHB).  B: Spatial distribution of m/z 551 (100 x 100 µm). 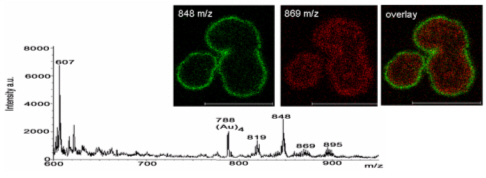 Metal assisted (Meta)-SIMS analysis of neuroblastoma cells. 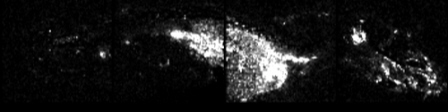 Whole-body rat sections: Image of heme signal (m/z 616) acquired on a whole-body Brown-Norway rat section. Grayscale ranging from 0 to 5000 (a.u.) 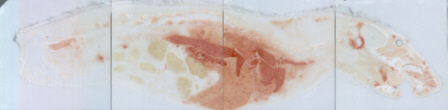 Optical image of the same section before matrix coating. The blood distribution matches well with the MSI signal. 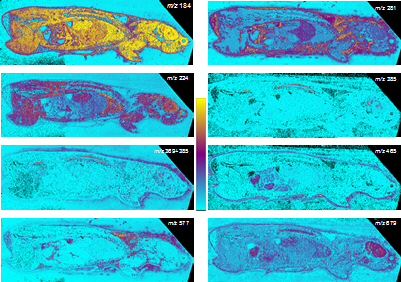 SIMS of a whole mouse section. Image acquired in the positive ion mode (left) and in the negative ion mode (right) with Bi3+ primary ions (6E8 ions/cm²), 84x28 mm², 768x256 pixels, pixel size 109 µm², acquisition time 12 h. no normalization. Different sample treatments protocols utilized by the partners are described and discussed. The aim of these treatments is to obtain, for molecular imaging, and in both MALDI and SIMS, the best sensitivity, with the lowest spatial delocalization of the compounds. In MALDI, the application of a matrix at the surface of the sample is mandatory, and different methods are now supplanting the original method in which the tissue surface was manually coated with an air sprayer. Some of these methods can also be transposed to SIMS in which the addition of a matrix on the surface is not always utilized. 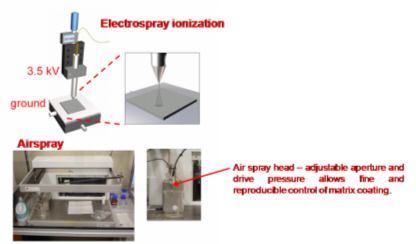 Apparatus used for matrix deposition in ME-SIMS. The airspray is also for MALDI experiments. 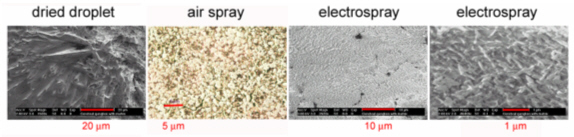 Comparison of the matrix coatings obtained using different deposition techniques.  Renal tissue coated with pneumatically assisted spray (Sinapinic acid, 1:1, v/v, MeCN/0, 2% TFA). At CNRS-Gif, a prototype of an automatic spotter has been developed in collaboration with a French company (Siliflow). The droplets are delivered by a patented piezoelectric ejector, having different nozzle diameters (80 & 150 µm), with different ejected droplet volume (1 & 6 nL, respectively). The ejector is connected to a syringe pump and all the sucking, ejection and rinsing steps are fully automated and computer controlled. The precise positioning of the droplet on the sample is performed by a computer controlled plate. This system is presently able to deposit several droplets of ~400 µm diameter (depending on the tissue, the sample support, etc) at the same position. 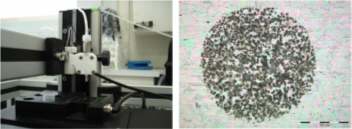 Piezoelectric droplet ejector developed by Siliflow for CNRS-Gif and sSinapinic acid droplet (3successive depositions) deposited at the surface of a rat brain section
|
| Next > |
|---|
